

For details on local printing requirements see. Requires the HP Smart app download and supported HP printer. Average timing savings comparison based on using printer and desktop scan software to complete similar scanning tasks. Average timing estimate based on: 1) downloaded HP Smart app on mobile or desktop device, 2) setting up Smart Tasks shortcut, 3) scanning jobs which have more than 2-3 tasks associated with them (scan to email, save and rename, store to cloud, etc.). Claim based on research of printer manufacturer’s mobile print apps and Keypoint Intelligence - Buyers Lab hands-on testing and study commissioned by HP. Market share as reported by IDC CYQ2 2018 Hardcopy Peripherals Tracker. Compared to OEM mobile printing apps for the majority of top-selling inkjet & laser printers & all-in-ones for home & home office, priced less than or equal to $429.99 USD.Certain features/software are available in English language only.

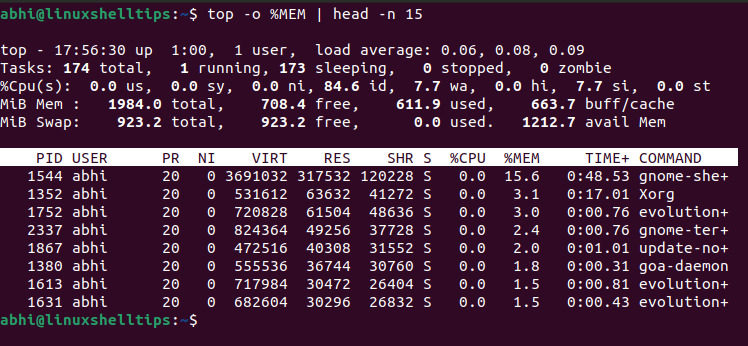
The data is continuously updated, which allows you to follow the processes in real-time. The top command is useful to check memory and CPU usage per process.
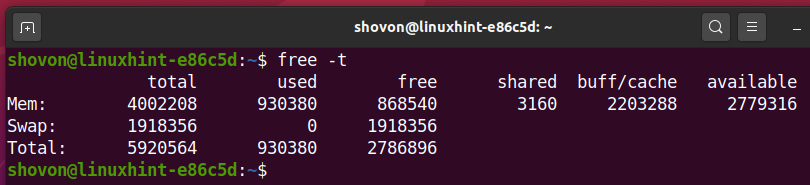
r: number of processes waiting for run time.The detailed description listed below provides an explanation for each value in case you need assistance in analyzing the results. The table below lists the most useful variations of the free command. The free command has multiple options to format the output so that it better matches your requirements. The key figure being the available value as it displays how much memory is still available for running new applications. Memory reserved by the OS to allocate as buffers when process need themĮstimation of how much memory is available for starting new applications, without swapping.Ĭompared to the /proc/meminfo file, the free command provides less information. Unused memory (free= total – used – buff/cache) Memory currently in use by running processes (used= total – free – buff/cache) The data represents the used/available memory and the swap memory figures in kilobytes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
